## fetch and merge origin
git fetch origin/master
git rebase origin/master
#push After rebase
git push --force-with-lease orgin branch1
git clean -fd: remove untracked directories / files.
#-fdL means force removal of untracked files and directories
#This will unstage all files you might have staged with git add:
git reset
#This will revert all local uncommitted changes (should be executed in repo root):
git checkout .
## Throw away all my staged and unstagged changes, forget everything on my current local branch and make it exactly the same as origin/master
git reset --hard origin/master
## reset a single file
git checkout HEAD -- file.txt
#restore one file from previous commit
git checkout xxxx(headID) -- file.txt
## Compare Branch
git diff branch1 branch2
## Move It can compare files rather than mark as delete and new
git mv file1 file2
## Add/stage by chunk of a file
git add --patch filename
## Revert PR Change
git revert commitID
git push -u origin branchName
初始化
#设置 global 变量会应用到所有之后建立的git repository
git config --global user.name "Becks"
git config --global user.email "becks@gmail.com"
#查看global变量
git config user.name
git config user.email
#初始化git repository
git init
#生成一个文件现在repository里,
touch 1.py #并没有添加到管理库当中
#查看当前文件状态, 可以发现哪些文件还没添加到管理空当中, 也可以显示现在修改的文件是不是跟上次commit比被modified
git status
git status -s #显示缩写的状态,红色的M表示还没stage, 绿色的M表示已经stage了
#如果当stage后, 没有commit, 又做了修改, 再git status, 会有两个M, 一个红色,一个绿色
#添加到管理库当中, 让文件变成stage 状态
git add 1.py #再使用 git status, 显示文件已经被可以提交修改了
git add. #把所有文件都stage
#提交修改 commit
git commit -m "create 1.py" #-m 自定义更改的信息
#不用add,直接commit; 必须是文件已经被融进仓库了,如果是新文件,还没被融进来,就不行
git commit -am "change 3 in dev"
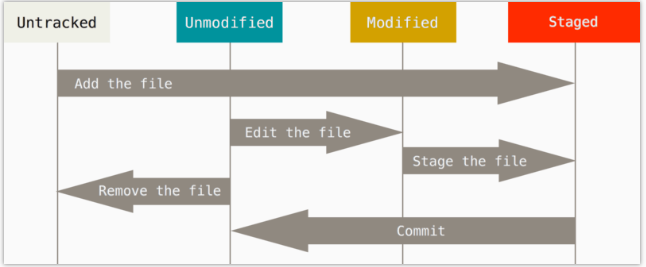
untracked: git 就根本不知道我们有这个文件,我们要把文件 添加到git 当中; add 文件 就到了staged 状态了, 然后就可以commit,commit之后就变成了unstaged 的状态; unmodified, modified 都是属于unstaged的状态
每次更改文件后需要到先到stage 状态 (git add)才可以commit
记录修改
git log #显示所有更改的commit的信息,比如commit两回,显示两次commit
git log --oneline #显示每个commit用1行
git log --oneline --graph #用图形的方式显示, 当只有一个分支, 会在commit前加上星号成一条线,
#显示现在文件和上次commit的不同
git diff #红色是之前的commit的, 绿色是现在文件
git diff --cached #当文件已经stage, git diff 显示不出不同,需要这句话,显示staged后的文件和上次commit的不同
#当文件stage, 没有commit, 又做了修改,需要下面cmd看不同,如果用git diff --cached,只会显示staged的部分,不会显示又更改的部分
git diff HEAD
当修改已经被stage (git add) 再看git diff是看不出不同的, 如想看不同需要git diff –cached
回到从前
reset
#本次commit 不会新建commit log,会融进上次commit 的log
# amend 把stage 状态放在上个commit当中, no edit是不更改上次commit的评论
git commit --amend --no-edit #改完之后发现message 没变,但是id是会变的
#返回从stage的状态 到modified的状态
git reset 1.py #把 1.py 返回unstaged的状态
#把commit的过后的版本返回到之前的状态, 调整head 到上一个,上上一个;
git reset --hard HEAD #把head 移到了移动到之前commit上面,remove所有本次的修改
#git status会显示没有任何修改了
git reset --hard HEAD^ #把head 移到前一个commit,
git reset --hard HEAD^^ #移到前两个commit
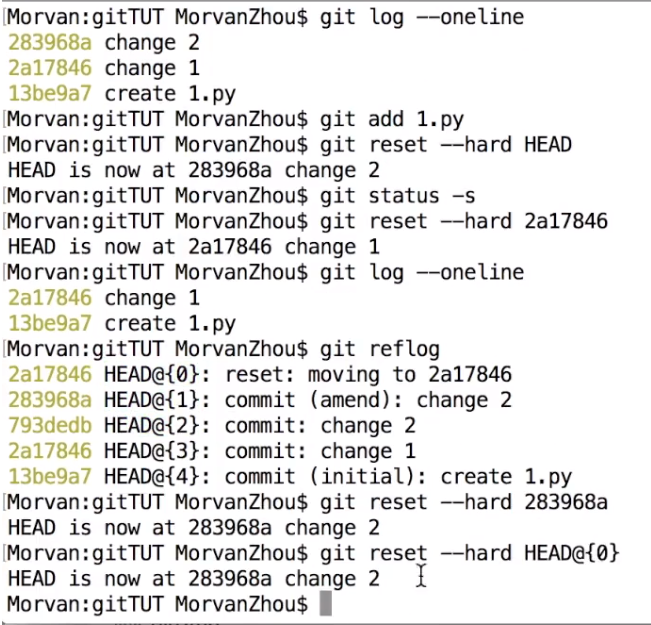
git reset --hard 7a7ecea #把head 移到 7a7ecea这个id上面去 (看id: git status --oneline)
#再git status --oneline 就不能看7a7ecea之后的commit的
## reset 几个file 到之前的head
git checkout 7a7ecea -- 1.py 2.py
## revert to head 之前一个commit
git checkout 7a7ecea~1 -- 1.py 2.py
#也可以把head回到未来, 从上上个移动到现在的
git reflog #看每一个的变化, 显示每一个head的移动
git reset --hard 3f27543 #通过reflog 找到想返回之后的head id,可以返回了
git reset --hard HEAD@{0} #也可以把之前复制过来
checkout
#只让一个文件回到过去
git checkout 7a7ecea -- 1.py # -- 只有有空格
#7a7ecea是之前commit的id, 只恢复1.py; 2.py 还是现在的状态
#之后修改再commit, 会建立新的commit的,git log --oneline 显示这次在过去的commit上面,过去的commit不会像reset一样消失
如果更改了file, 但还没有stages, 可以用恢复当前的files
git checkout .
管理分支
比如master是client用的,要稳定版,自己要用一个开会的分支
#方法一:
git branch dev #建立一个名为dev的,head还在master
git checkout dev #head切换 dev, 再git branch, dev分支上显示星号
#方法二
git checkout -b dev #建立一个名为dev的, 并把head移动到dev分支上
#查看分支
git branch #显示现在所有的分支, 星号表示现在的分支
#删除分支
git checkout master
git branch -d dev #删除dev的分支, 报错,因为现在就在dev分支上, 先切换别的分支,才能删除
git branch -D dev #如果git branch -d dev, 大写的D表示强行删除
# Merge
git checkout master #保证在master上,merge时候不能在dev branch上
git merge --no-ff -m "keep merge in info" dev
#把dev merge到master上来, -m "keep merge in info"把信息记录在log
# --no-ff, no faster forward, 默认是faster forward是不会留信息
#merge 之后再看git log --oneline --graph #会有图像显示branch的分支产生,merge
分支冲突
Merge
比如 两个分支master, dev各有修改, 当git merge dev 时候有conflict, 然后file里显示什么冲突了
- 把冲突的部分删除掉,做修改,修改过后的状态是modified,
- 方法一: stage (git add .) 再commit(git commit -m “solve conflict”)
- 方法二: 直接 git commit –am “solve conflict”
- 再git log –oneline –graph 会显示两个分支合并了
在master 和 dev上有改变,然后合并了两个分支
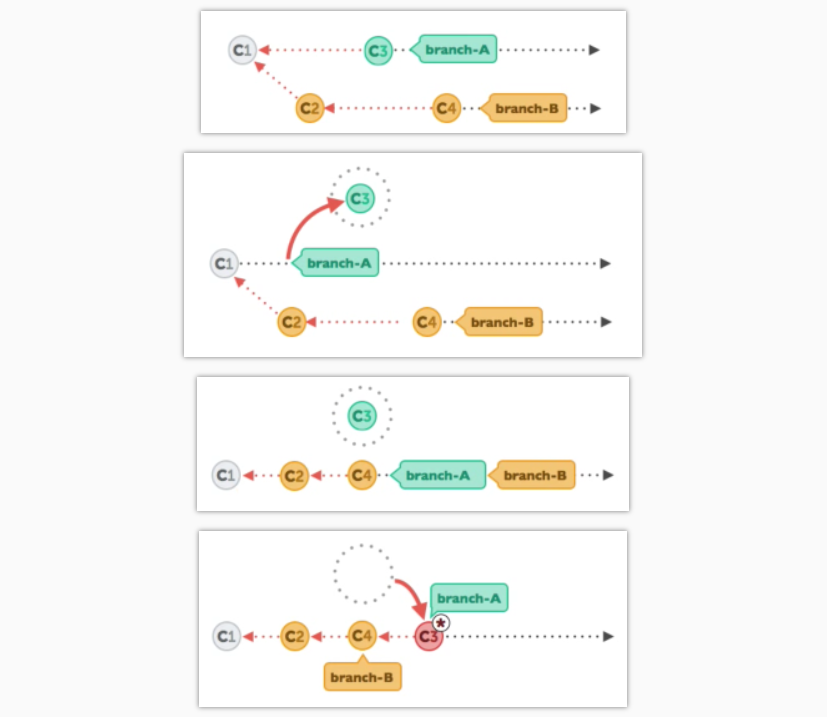
rebase : 重新基于主分支的内容
Branch B 为主分支,然后有天有人提交了bug的修改, 在主分支branch b的上进行了提交,
比如我在branch A上工作,在c3, 这时如果想把bug融合到c3上;
方法是: 先把branch A的c3拿走,空出来, 把c2,c4合并到上面去, 再把c3放到合并以后的地方, 注:现在c3基于c4, 以前的c3不复存在了 所以rebase是危险的方式, rebase 后c3的commit id和rebase前c3的id是不一样的
#先checkout master,然后再主分支的修改基于dev的修改 (上图的branch A是master, branch b是dev)
git checkout master
git rebase dev #(把master分支基于dev分支)
#如果有conflict, 跟merge一样的, 去修改conflict
#修改完conflict, git branch 发现不在master 和dev的任何一个分支上, 在一个新的分支上rebasing master上
#stage + commit
git add 1.py
git rebase --continue #继续rebase
#如果碰到conflict,想放弃rebase
git rebase --abort
git log --oneline --graph #会发现dev的commit插到master上面来了,
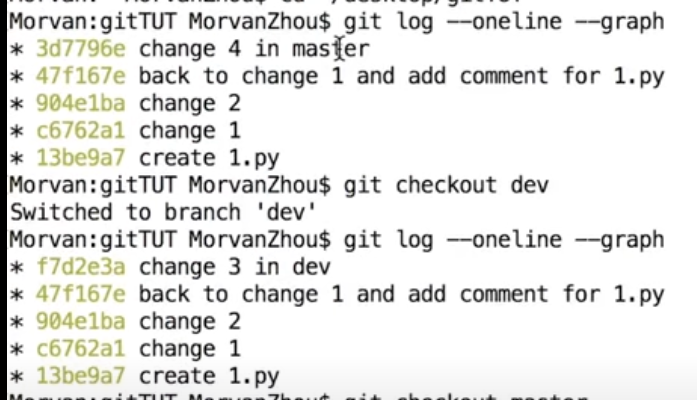
最上面是master 的log, 下面的是dev的log
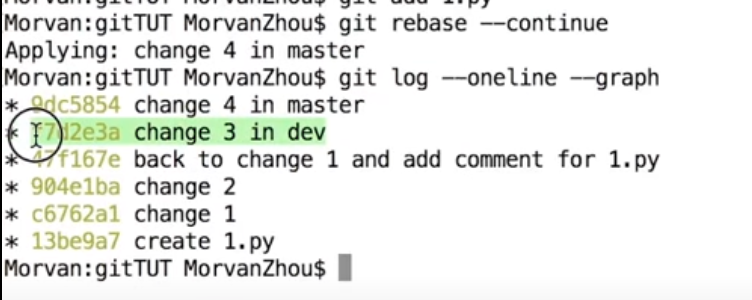
rebase 和 merge 不一样,dev上commit 的内容被插进master的分支上, 而不是分成两个branch 再merge, c3重新基于刚修改的dev的分支,注意change4 master的ID 和 之前的ID不一样的
临时修复
比如要改之前的程序, 而现在的改进程序还没有完成, 不想把改进的和要改的程序放在一起, 用stash可以改进的code暂存一下而不用commit。 等改后之前的, 再继续工作, 有不同的commit, 不会有冲突
git checkout dev
#git status -s 显示文件已经被更改
git stash #把现在的文件放在缓存区
git status -s #此时就没有任何的modified 文件了

stash之后,看status不会显示modified的内容
#此时接到电话,给老板写代码
#此时再建一个新的branc: git checkout -b boss; 在这个branch中修改之前的code, stash缓存的更改不会建立在这个branch中
#修改完boss分支后, 再checkout 回dev:
git checkout dev #回到dev,显示上次commit的内容,不会显示上次修改stash的内容
git stash pop #就会把之前修改暂存的返回回来
当stash后再建立新的branch, stash缓存的内容不会出现的新的branch中, 新的branch只显示上次commit 的内容
GitHub
git push -u origin master #把master分支推到origin上面, origin指得是online的管理库
git push -u origin dev #把dev分支推到origin上面
git config --get remote.origin.url #查看remote url
#修改已经存在的origin为新的http://....
git remote set-url origin https:// #已经有remote url,改变现有的url
git remote add origin https:// #初始url
origin指得是online的管理库, history显示所有的改变, change显示每次commit发生变化, 本地的.git文件也被上传到管理库