Config in Mac
use keyboard input Command + Shift + P then type cmcon to choose cmake c++ kits
If Show Error to configuring project,
- Check if Cmake installed. Run
cmake --version. If not installbrew install cmake - Check if brew is in path; Check if
/etc/pathshas/opt/homebrew/bin, if not, add it at the end.
aux_source_directory(. SRC_DIR) 会查找指定目录下的所有源文件, 这里查找 . (current directory), 并查找结果存进SRC_DIR
file(glob variable_name file): Generate a list of files that match the globbing-expressions and store it into the variable.
option (USE_MATH “Use provided math implementation” ON): Provide an option for the user to select as ON or OFF. If no initial value is provided, OFF is used. “Use provided math implementation” 使用来help string describing option
Executable
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.14.5) #VERSION 必须大写,否则报错
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0) #PROJECT CALL是必须的
add_executable(cmake-good main.cpp) #make exectuable, 生成exe会叫cmake-good
Make: is a buildsystem: it drives the compiler and other build tools to build your codeCameis a generator of buildsystem. It can produceMakefiles. It can produce Ninja build files, it can procde KDEvelop or Xcode projects.
#Step1 : build CMakeFiles
cmake . #引用source directory
#build exe
cmake --build . #引用already configured binary directory, 必须要有cache的文件, cache文件会由cmake . 生成
# windows 环境中 会把exe 建立在Debug folder 中, 因为默认是DEBUG
cmake --build . --config Debug
#等同于上边的command,
#cmake will run underlying msbuild tool to build VS Solution
# Step 2:
make
Linked a library
比如下面C++ header 和cpp 文件
//---------------hello.h
namespace Hello{
void sayhello();
}
//---------------hello.cpp
#include "hello.h"
#include <iostream>
void hello::say_hello(){
coud << " hi "<<endl;
}
//---------------main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "hello.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
hello::say_hello();
}
如果这么按照上面的方式executable 那么写cmake, run exe时候会有link error, 解决方法是加上add_library 和 target_link_libraries,
add_library() 第一个参数是link library名字(可以随意建立) + library 模式(static or shared), 第二个参数 是头文件,第三个参数 cpp文件
target_link_libraries() 第一个参数是executable, link到谁, 第二个参数是link interface mode, 第三个参数 被link的library
find_package(xxx [version] [QUITE] [REQUIRED]) import xxx module. Find and load settins from an external project. pull all of toolchain details, such as the names and locations of the compilers, which branch to built against, and where libraries canbe found and should always be required.
- REQUIRED option stops processing with an error message if the package cannot be found.
- QUITE deisable informational messages
- [EXACT] : request that the version be matched exactly.
加上add_library 和 target_link_libraries run cmake –build . (on windows) or make (on linux), 不用run cmake . , 因为会automatically detect 如果CmakeLists.txt 被更改了 (out of date), 如果更改了,会自动run cmake .
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.14.5) #VERSION 必须大写,否则报错
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0)
add_library(
say-hello #创建一个link library
hello.h
hello.cpp
)
add_executable(cmake-good main.cpp) #make exectuable, 生成exe会叫cmake-good
target_link_libraries(cmake-good PRIVATE say-hello) #把建立的library 和main link到一起
#第一个argument是executable, link到谁, 第二个argument是link interface mode, 第三个argument 被link的library
再run Debug\cmake-good.exe 会打印出我们想要的结果
注: we don’t specify the type of library, but it build a static library(default), 如果我们specified SHARED, 如下面,就会建立一个shared linked library
add_library(
say-hello SHARED #创建一个shared linked library
hello.h
hello.cpp
)
add_library(
say-hello STATIC #创建一个static linked library
hello.h
hello.cpp
)
在linux 上,ldd 可以看linker dependency of lib, 如果是shared library, ldd 可以看见libsay-hello (我们上面创建的lib)的dependency, 如果是static, ldd就看不见这个library
ldd cmake-good
我们可以更改add_library static library的选项 成shared, 通过cmake -D BUILD_SHARED_LIBS=TRUE . , 即使我们不声明add_library 成shared, 也会生成shared library
cmake -D BUILD_SHARED_LIBS=TRUE .
Make library
Set VERSION property (optional but it is a good practice):
set_target_properties(mylib PROPERTIES VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION})
You can also set SOVERSION to major number of VERSION. So libmylib.so.1 will be a symlink to libmylib.so.1.0.0.
set_target_properties(mylib PROPERTIES SOVERSION 1)
Declare public API of your library. This API will be installed for third-party application. It is a good practice to isolate it in your project tree (like placing it include/ directory). Notice that, private headers should not be installed and I strongly suggest to place them with the source files. 定义public header
set_target_properties(mylib PROPERTIES PUBLIC_HEADER include/mylib.h)
If you work with subdirectories, it is not very convenient to include relative path like “../include/mylib.h”.(不希望让include header时候 加上relative path e.g. #include “../include/mylib.h”) So, pass top directory in included directories:
target_include_directories(mylib PRIVATE .)
CMake Function
File
file(glob variable_name filelist<globbing-expression>): 产生一个list of files that match globbing-expression 类似 regular expression 并 store it into the variable
Note: We do not recommend using GLOB to collect a list of source files. 因为如果CMakeLists.txt 没有更改时候,但是a source is added or removed then generated build system cannot know when to ask CMake to regenerate.
e.g. Developer A add new file x.c 但是A没有change CMakeLists.txt and commit after he finished implementing x.c. Now Developer B git pull, 因为没有modifications to the CMakeLists.txt. CMake 不会run again and B causes linker errors when compiling. 因为x.c 没有added to its source file list.
如果加了file(GLOB ...)需要run 下面的 every time you add or delete a source file
cmake <your_source_dir> -G <your_build_generator>
Examples of globbing expression 包括
*.cxx - match all files with extension cxx
*.vt? - match all files with extension vta,...,vtz
f[3-5].txt - match files f3.txt, f4.txt, f5.txt
CMAKE in Visual Studio
MSBUILD
ZERO-CHECK: check if CMAKE configuration file is out of date and needs to regenerate VS studio project. All projects will depend on ZERO CHECK project. You can aslo build ZERO CHECK within Visual Studio itself to regenerate the configuration within visual studio without building any projects
当compile project, can run as executable by right-click set as start project then start debugger.
当在visual studio 里面更改Debug 到release, 不用重新run cmake 直接build project即可, cmake will run the underlying msbuild build tool in order to build this visual studio solution. Cmake natively understands how to drive MS build to build generated projects. It means you can using Visual studio Solution even without having installation of Visual studio. <span “background-color:#FFFF00”> Visual C++ build tools are sufficient to generate and build Visual Studio Solutions without having the actual IDE installed (Visual C++ 足够generate solution 即使没有装IDE).</span>
We can also build specific targets by using – target flag
cmake --build . --config Debug target simple
可以在CMakeLists.txt 文件夹中右键open in visual studio. Visual Studio detects the CMakeLists.txt and open natively without any special commands needing to be run. It show file structure in solution Explore as if it had generated a real solution. Visual Studio Output windows 中可以看见 Visual Studio会自动run cmake for us and generate ninja
NINJA
CL.exe
Visual C++ 可以是 MSVC or microsoft visual C++ 缩写. 就像GCC and clang, visual C++ 也有 a command line called CL.EXE and the linker is called link.exe, 如果装了Visual C++, 可能有很多的CL.exe 和 Link.exe, target不同的platform
比如run下面的会报错,因为unlike GCC and Clang, CL.exe has no built-in default include path. You need to either set in command line or special environment that CL.exe will check and use when it does the search. 最简单的方法set environment is to use Visual Studio Developer Command Prompt, 打开它会显示Environment initialized, 因为它include batch file that set the environment variables necessary to compile and link programs, 在Developer Command prompt 就可以run: cl main.cpp (we don’t generate any build system, and compile and link to this program manually by executing cl main.cpp )
#在普通command prompt中run 会报错
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.21.27702\bin\Hostx64\x64\cl.exe" main.cpp
#在developer command prompt run
cl main.cpp
#developer command prompt 中
pwsh #切换到powershell
ls Env: #查看所有的environment variable
echo $$env:INCLUDE$ #可以看developer command prompt的include path
echo $$env:LIB$ #可以看developer command prompt linker search library path

vcvarshall
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvarsall.bat" x64
#在普通command 上run 这个会切换到与developer command prompt中一样的environment vairable
#CL.exe is on path and ready is use
nmake
nmake is a partial reimplementation of standard UNIX make, go to cmake project folder (有CMakeLists.txt的), build using nmake. Nmake instead of producing MSBuild file, it will produce nmake format files that can be executed with nmake。 Then ask nmake to build cmake executable for us (与cmake build 花的时间差不多),
NMake 和 CMake 花的时间都挺长的,可以用NINJA, 有可能报错if GCC or Clang in your path 因为NINJA called GCC compiler, because NINJA is a make file generaterator 即使ninja doesn’t emit make file style build files, 需要specify CMAKE_C_COMPILE 是CL
NINJA 最快,因为during compilation tests, CMake generates a small C make project and tries to build and compile it. Ninja is inherently much faster because it’s targeted specifically at compiling large numbers of source files in parallel as much as it can. (Ninja 被用于Chrome project to build webbrowser 因为Chrome 有enormous number of source files)
Using NINJA:Github download NINJA, 需要把NINJA add to system search path
#Load Environment Variable
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvarsall.bat" x64
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -G "NMake Makefiles" .. #using nmake as target generator #产生cmake files
nnamke cmake #build cmake executable using name
cmake .. (与cmake build 花的时间差不多)
#用NINJA Build
cmake -G Ninja ..
#specify compiler
cmake -G Ninja -DCMAKE_C_COMPILE=cl -DCMAKE_C_COMPILE = cl .. #产生cmake files
ninja cmake #build project
Summary: Visual Studio Configure 最慢, NMAKE configure 第二慢, Ninja Configure 最快
Visual Studio Code
下载extension cmake (provide by twxs to support syntax highlight ) & cmake tools (it provide extra feature and tweaks helped support cmake based project in editor), 然后点view -> command palette -> 输入 cmcon (Cmake configure) 选择想要的compiler
Subdirectory &Target
add_subdirectory 会include subdirectory的CMakeLists.txt
/*------------------Hello.h---------------------*/
namespace hello
{
void say_hello();
};
/*------------------Hello.cpp---------------------*/
#include "hello.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void hello::say_hello(){
cout << " hi "<<endl;
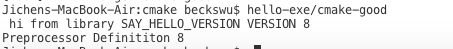
cout<< "Preprocessor Definititon "<< SAY_HELLO_VERSION <<endl;
//SAY_HELLO_VERSION 来自CMAKE 的definition
}
/*------------------main.cpp---------------------*/
#include <iostream>
#include "say-hello/hello.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
hello::say_hello();
system("Pause");
cout<< "Preprocessor Definititon "<< SAY_HELLO_VERSION <<endl;
}
建立如下面的folder
say-hello
-- src
--say-hello
--hello.h
--hello.cpp
-- CMAKELISTS.txt (1)
hello-exe
-- CMAKELISTS.txt (2)
-- main.cpp
CMAKELISTS.txt (3)
CMAKELISTS.txt (1)
定义target_compile_definitions 好处是,不用修改code, 直接这里改,然后一build 就好了
PUBLIC: 如果target_compile_definitions 定义成了PUBLIC, 谁都可见, PUBLIC says both we and our consumers recieve the value.
PRIVATE: 如果target_compile_definitions 定义成了PRIVATE, 只有这个library 可以看见,其他的library 还有main function 都看不见
INTERFACE: 如果target_compile_definitions 定义成了INTERFACE, 除了这个library 其他的library都可见, 因为INTERFACE has the opposite effect of PRIVATE, only consumers receives this value properties but we ourself do not
add_library(
say-hello #创建一个link library
src/say-hello/hello.h #让path match relative to CMakeLists.txt
src/say-hello/hello.cpp #让path match relative to CMakeLists.txt
)
#因为main 与 hello.h 不在一个文件夹,所以要把hello.h include 到search path
target_include_directories(say-hello PUBLIC "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src")
#PUBLIC 是 interface mode
#${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} refer to the directory process 现在这个cmakelists, 就是say-hello 这个directory
target_compile_definitions(say-hello PUBLIC SAY_HELLO_VERSION=8)
#set preprocessor version = 8
#相当于#define SAY_HELLO_VERSION 8 在C++中
#因为set 了public, SAY_HELLO_VERSION will propagate to everyone who link to it
#target_compile_definitions(say-hello PRIVATE SAY_HELLO_VERSION=4)
#target_compile_definitions(say-hello INTERFACE SAY_HELLO_VERSION=4)
CMAKELISTS.txt (2)
add_executable(cmake-good main.cpp) #make exectuable, 生成exe会叫cmake-good
target_link_libraries(cmake-good PRIVATE say-hello) #把建立的library 和main link到一起
#第一个argument是executable, link到谁, 第二个argument是link interface mode, 第三个argument 被link的library
CMAKELISTS.txt (3)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.14.5) #VERSION 必须大写,否则报错
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0)
add_subdirectory(say-hello) #say-hello 是directory的名字
#会include subdirectory的CMakeLists.txt
add_subdirectory(hello-exe)
#因为hello-exe中的main call 了 say-hello 中的header 所以需要放在后面
#还以为hello-exe中的CMakeLists.txt的target_link_libraries call 了say-hello library
Build 后 run的结果
- message: to print on screen
- status: is one of enum argument represent the mode of printing
- 单引号括variable 会当成单引号, 双引号括 variable 会当specifier
- set : 给VARIABLE 设置变
- {PROJECT_NAME}, ${PROJECT_VERSION}, call project name & version from Project command
set(my_variable 123)
message(STATUS "${my_variable}") #打印 123
message(STATUS '${my_variable}') #打印 '123'
Scripting
The only type in cmake is string. Everything is string. 一行内argument 不同的string 用空格隔开,多少空格都可以,可以move and shift whitespace
command_name(LIST OF ARGUMENT) #command is a function. you cannot have two command on the same line, it’s a syntax error
message(STATUS “”) 打印到屏幕
set(MY_VARIABLE “123”) 给VARIABLE 设置变量
${PROJECT_NAME}, ${PROJECT_VERSION}, call project name & version from Project command
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
#Everything you pass is a string
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0) #MyProject, VERSION, 1.0 are all string
#project("MyProject" VERSION 1.0) #跟上面是一样的
# 我们不put comma between string, put whitespace, whitespace 可以被move and shift as we need
#project("MyProject" VERSION
# 1.0) 也是可以的
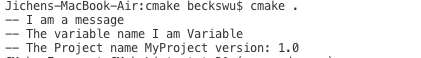
message(STATUS "I am a message") #message(STATUS) 就是 print message, 会打印I am a message
# " 引号是需要的,因为prevent pass each argument as separate item,
# 如果去掉引号,run cmake. 会显示Iamamessage , all argument together with no space
set(MY_VARIABLE "I am Variable") #set variables
message(STATUS "The variable name ${MY_VARIABLE}") #需要${} 去print variable
#${MY_VARIABLE} pass variable inline into the whole string before print message
message(STATUS "The Project name ${PROJECT_NAME} version: ${PROJECT_VERSION}")
#pass project from most recent project call and call project Version 来自Project call
输出
if
- if(${my_bool} ) 和 if(my_bool) 作用一样,都是deference varaible my_bool
- NOT: to negate. e.g. if(NOT my_bool)
- Cmake treat一些string pattern as true, 其他的as false, 具体的pattern 在documentation
- AND, OR, LESS : logical
- Difference between STREQUAL, EQUAL is : EQUAL do the arithmatic comparison, STREQUAL is do string comparison
- elseif(MY_STRING MATCHES “string$”) : “MATCH regularization, match if string is the end of MY_STRING
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0)
set(my_bool, TRUE)
if(my_bool) #cmake treat this unquoted argument as variable reference my_bool,
#if(${my_bool} ) 与if(my_bool) 一样
#if(NOT my_bool) Not is to negate condition
#if("TRUE") #string literal true, CMake intepret as true condition
#if("FALSE")
message(STATUS "Condition was met")
else()
message(STATUS "Conditional failed")
endif()
#--------------_String Compare-------------
set(MY_STRING "This is a string")
set(MY_OTHER_STRING "This is a string")
if(MY_STRING ) #Cmake treat一些string pattern as true, 其他的as false
message(STATUS "String (a) Condition was met")
else()
message(STATUS "String (a) Conditional failed")
endif()
set(my_value 1)
if(MY_STRING STREQUAL MY_OTHER_STRING ) #Cmake treat一些string pattern as true, 其他的as false
#具体的见cmake documentation
#if(MY_STRING STREQUAL "MY_OTHER_STRING" ) 如果加了引号cmake will treat it as string not variable
#if(NOT MY_STRING STREQUAL MY_OTHER_STRING ) NEGATE
message(STATUS "String(b) Condition was met")
else()
message(STATUS "String(b) Conditional failed")
endif()
if((MY_STRING STREQUAL MY_OTHER_STRING ) AND (my_value EQUAL "3"))
#Difference between STREQUAL, EQUAL is : EQUAL do the arithmatic comparison
message(STATUS "String(c) Condition was met")
elseif(MY_STRING MATCHES "string$") #match if string is the end of MY_STRING
#MATCHES is regular expression
message(STATUS "String(c) string is the end of MY_STRING")
else()
message(STATUS "String(c) Conditional failed")
endif()

While
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0)
set(MY_STRING "This is a string")
set(MY_OTHER_STRING "This is a string")
set(my_value 1)
while(my_value LESS 10)
message(STATUS "VALUE is ${my_value}")
math(EXPR my_value "${my_value} + 1")
#EXPR always是第一位, 第二个参数是store的, 第三个是math expression
endwhile()

For Loop
Loop Mode
- IN ITEMS : 加LOOP 的ITEMS
- RANGE : 可以加数字 — LIST : 用from list
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0)
set(MY_STRING "This is a string")
set(MY_OTHER_STRING "This is a string")
set(my_value 1)
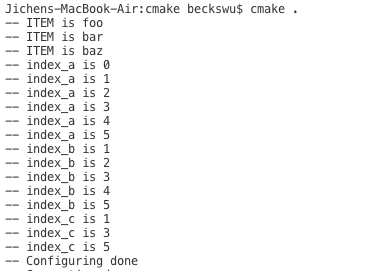
foreach(item IN ITEMS foo bar baz ) #第一个参数 is loop variable, 第二个参数是 loop mode: IN ITEMS
message(STATUS "ITEM is ${item}")
endforeach()
foreach(idx RANGE 5) #loop from [0,5] inclusive
message(STATUS "index_a is ${idx}")
endforeach()
foreach(idx RANGE 1 5) #loop from [1,5] inclusive
message(STATUS "index_b is ${idx}")
endforeach()
foreach(idx RANGE 1 5 2) #loop from [1,5] inclusive, step is 2
message(STATUS "index_c is ${idx}")
endforeach()
Property
CMake passing argument property: automated list expansion. List in cmake is semicolon lists of values (e.g. 1;2;3)
- set_property
- GLOBAL: first argument . 设置property 为cmake property behave like ENUM argument
- DIRECTORY: first argument . 设置property为 directory property,只能用get_property 接
- PROPERTY: is key word specifier for argument
- PROPERTY FOO: is the value of keyword argument property
- get_cmake_property: get value from GLOBAL Scope property to assign to variable
- get_property: 用来接DIRECTORY property
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0)
#property is different from variable
set_property( #set property at global scope called foo
# PROPERTY FOO 1 2 3 are all separate string argument,
GLOBAL #GLOBAL behave like ENUM argument
# "GLOBAL" #如果用引号和不用引号一样,因为是string argument
PROPERTY FOO #PROPERTY is key word specifier for argument FOO
#FOO is the value of keyword argument property
1
2
3
)
#foo_value 用; separate element from list
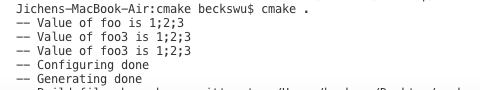
get_cmake_property(foo_value FOO) #get value from property
message(STATUS "Value of foo is ${foo_value}") #打印Value of foo is 1;2;3
set_property(
DIRECTORY #set the property foo on the directory,
#所以在这个程序里面 get_cmake_property, 会显示FOO2 not found
#因为我们没有cmake property FOO2, we have directory property
PROPERTY FOO2
1
2
3
)
#也可以把list传入property
set(my_list 1 2 3)
set_property(
GLOBAL
PROPERTY FOO3
'${my_list}'
)
get_cmake_property(foo_value3 FOO) #get value from property
message(STATUS "Value of foo3 is ${foo_value3}") #打印Value of foo is 1;2;3
set(target GLOBAL) #GLOBAL HERE is not specifical behavior
# this is set the value of target to string "GLOBAL"
set_property(
"${target}" #可以把string 传入作为GLOBAL
PROPERTY FOO4
"${my_list}"
)
set(target DIRECTORY "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}") #可以set directory 具体的位置 作为list
#to set property on the project source directory
set_property(
#'${target}' #这么写会报错,因为这么写会写成 DIRECTORY; \work\src 的格式,有个分号
${target} #这么写 会自动list expansion in place
PROPERTY FOO5
"${my_list}"
)
get_property(foo_value5 ${target} PROPERTY FOO5 ) #get value from property
# ${target} do the list expansion in place
message(STATUS "Value of foo3 is ${foo_value5}") #打印Value of foo is 1;2;3
Function
- 第一个argument is function, 随后的argument is argument name
- 当call function 时候, must pass at least the number of argument declared in the function, function declared 几个参数 call时候只能多 不能少
- 当function 不知道pass 了几个argument 时候可以用ARGV ARGN, ARGV: 所有传进function的参数都在ARGV 或者 ARGN当中。 不同点是ARGV 是包括了传入function 所有参数(all variable), ARGN只包括传入function 除了function declare 的参数外的参数(argument have not been bound to a named argument to the function)
- 当定义GLOBAL variable, 可以定义在任何地方,因为global variale被function called 的时候才做expansion
- the variable scope of a function is initially copied from the variable within the parent scope. 当call function, cmake will make a copy of entire parent variable scope and set into function call。 当function called 完, restore the original global scope. 这意味着改global variable inside function will not change variable outside function except explicitly set to change original
- 注:下面例子中 set(MY_GLOBAL_VAR 13 PARENT_SCOPE) 只会改变parent scope 变量,但不会改变current scope 的变量,因为我们没有改copy的,只改了original的
- function 以 参数pass 的时候,相当于set, 见下面例子
function(increment var)
#function 用过variable 来called, 相当于等于 set(var, value)
message(STATUS "VALUE before increment is ${var}") #print value
message(STATUS "VALUE after increment is ${${var}} ")
#we deference once to get value, we deference again to get 14
endfunction()
set(value 14)
increment(value)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
project(MyProject VERSION 1.0)
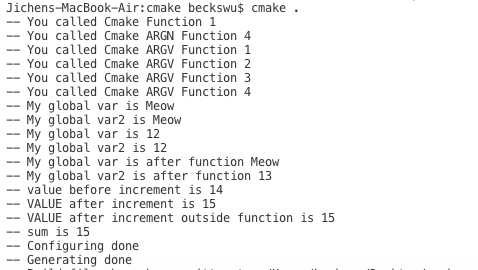
function(do_cmake_good first_arg) #First Argument is function name, subsequent argument is function 参数
message(STATUS "You called Cmake Function ${first_arg}")
endfunction()
#function declared 几个参数 call时候只能多 不能少
do_cmake_good(1 2 3 )#I can pass more argument,
#first_arg is bound to 1, 但是 2, 3, 4 不bound any variable in the function
function(do_cmake_good2 first second third)
foreach(arg IN LISTS ARGN) #ARGN 会从第四个参数开始
message(STATUS "You called Cmake ARGN Function ${arg}")
endforeach()
foreach(arg IN LISTS ARGV) #ARGN 会从第一个参数开始
message(STATUS "You called Cmake ARGV Function ${arg}")
endforeach()
endfunction()
do_cmake_good2(1 2 3 4 )
function(do_cmake_good3)
message(STATUS "My global var is ${MY_GLOBAL_VAR}") #print Meow
#expansion happens only when actually evaluate
message(STATUS "My global var2 is ${MY_GLOBAL_VAR2}") #print Meow
set(MY_GLOBAL_VAR 12)
message(STATUS "My global var is ${MY_GLOBAL_VAR}") #print 12
set(MY_GLOBAL_VAR2 13 PARENT_SCOPE) #会改变parent scope 的variable
#但是不改变its current scope
message(STATUS "My global var2 is ${MY_GLOBAL_VAR}") #print MEOW
endfunction()
set(MY_GLOBAL_VAR Meow) #即使global variable定义在function的后面
#varaible 也可以expand 到function
set(MY_GLOBAL_VAR2 Meow)
do_cmake_good3()
message(STATUS "My global var is after function ${MY_GLOBAL_VAR}") #print Meow
#因为cmake called function时候, 是copy variable from parent scope,
# 而不是带着global variable在function 里面跑
message(STATUS "My global var2 is after function ${MY_GLOBAL_VAR2}") #print 13
function(increment var)
#function 用过variable 来called, 相当于等于 set(var, value)
# message(STATUS "VALUE before increment is ${var}") #print value
message(STATUS "value before increment is ${${var}}")
math(EXPR new_value "${${var}} + 1")
message(STATUS "VALUE after increment is ${new_value}")
#we deference once to get value, we deference again to get 14
set("${var}" "${new_value}" PARENT_SCOPE) #用scope 改变function 外面value的值,
#因为set(var, value) value = ${var}
endfunction()
set(value 14)
increment(value)
message(STATUS "VALUE after increment outside function is ${value}")
function(sum out a b)
math(EXPR ret "${a} + ${b}") #新variable ret = a + b
set("${out}" ret)
endfunction()
sum(value 5 3) #把 5 + 3 assign 给 value
message(STATUS "sum is ${value}")
Source/Binary Directories
File Structure, C文件与之前一样,没有更改
建立如下面的folder
say-hello
|
+--- src
|
| +--- say-hello
| |
| +--- hello.h
| |
| +--- hello.cpp
|
+--- CMAKELISTS.txt (1)
hello-exe
|
+--- CMAKELISTS.txt (2)
|
+--- main.cpp
CMAKELISTS.txt (3)
PrintVariable.cmake
CMAKELISTS.txt (1)
project(HelloLibrary VERSION 1.3.9)
add_library(
say-hello
src/hello_lib/hello.h
src/hello_lib/hello.cpp
)
target_include_directories(say-hello PUBLIC "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src")
target_compile_definitions(say-hello PUBLIC SAY_HELLO_VERSION=8)
CMAKELISTS.txt (2)
project(HeloProgram VERSION 2.0.1)
add_executable(cmake-good main.cpp)
print_variable()
target_link_libraries(cmake-good PRIVATE say-hello)
CMAKELISTS.txt (3)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15)
project(TopProject VERSION 2.0)
include(PrintVariables.cmake) #include 额外的Cmake Script
#print_variable() #call function from PrintVariables.cmake
add_subdirectory(say-hello example-binary-subdir)
#可以pass 第二个argument 作为binary build directory instead of default binary directory generated
add_subdirectory(hello-exe)
PrintVariables.cmake
#Project calls in sub directories do not affect the value of project
#named project version, project source, binary dir in the parent directory.
function(print_variable)
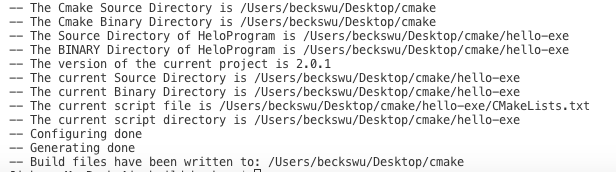
message(STATUS "The Cmake Source Directory is ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}")
#SOURCE DIR is top level of source tree
message(STATUS "The Cmake Binary Directory is ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}")
#BINARY DIR is top level of build tree
message(STATUS "The Source Directory of ${PROJECT_NAME} is ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}")
message(STATUS "The BINARY Directory of ${PROJECT_NAME} is ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}")
message(STATUS "The version of the current project is ${PROJECT_VERSION}")
message(STATUS "The current Source Directory is ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}")
#CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR directory of current CmakeLists.txt
message(STATUS "The current Binary Directory is ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}")
message(STATUS "The current script file is ${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_FILE}")
message(STATUS "The current script directory is ${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}")
endfunction()
run cmake. give output
Example
Same Folder
./Demo2
|
+--- main.cpp
|
+--- MathFunctions.cpp
|
+--- MathFunctions.h
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15.0)
project(DEMO, VERSION 1.0.0)
#aux_source_directory 会查找指定目录下的所有源文件,
#这里查找 . (current directory), 并查找结果存进SRC_DIR
aux_source_directory(. SRC_DIR)
add_executable(DEMO ${SRC_DIR})
Library in Sub Folder
./Demo3
|
+--- main.cpp
|
+--- math/
|
+--- MathFunctions.cpp
|
+--- MathFunctions.h
|
+--- CMakeLists.txt (1)
|
+--- CMakeLists.txt (2)
CMakeLists.txt (2),add_subdirectory 指明本项目包含一个子目录 math,这样 math 目录下的 CMakeLists.txt 文件和源代码也会被处理, target_link_libraries 指明可执行文件 main 需要连接一个名为 MathFunctions 的链接库 。
cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 2.8)
# 项目信息
project (Demo3)
# 查找当前目录下的所有源文件
# 并将名称保存到 DIR_SRCS 变量
aux_source_directory(. DIR_SRCS)
# 添加 math 子目录
add_subdirectory(math)
# 指定生成目标
add_executable(Demo main.cpp)
# 添加链接库
target_link_libraries(Demo MathFunctions)
CMakeLists.txt (1)
# 查找当前目录下的所有源文件
# 并将名称保存到 DIR_LIB_SRCS 变量
aux_source_directory(. DIR_LIB_SRCS)
# 生成链接库
add_library (MathFunctions ${DIR_LIB_SRCS})