Internal or external command are buildin to cmd.exe command. Batch let you run program within the shell. cmd.exe inside C:/Windows/System32
如果直接双击 batch script without pause, it 可能闪退 without letting you see the output
mkdir dir1: make directory named as dir1
cd .. : jump back to the parent directory
rmdir dir1 : remove directory named dir1, 如果directory不是empty, 显示error: The directory is not empty.
rmdir /S : removes everything inside the folder 包括folder, used to remove a directory tree.
rmdir /S /Q : Quiet Mode, 功能与rmdir /S一样,但是不会问是不是要remove directory tree.
del dir1 : delete everything inside the folder,但是不会delete folder,需要再call rmdir dir1 去remove the folder
move : move [Y : /-Y] [path1]filename1 [path2]filename2 , 如果path1等于path2, 那么move 也等于rename, /-Y flag: 不让prompt confirm 当overwrite file的时候, /-Y prompt会confirm是不是要overwrite file
copy copy source destination : destination可以只是path,不用说具体名字,那么copy时候会保持文件/文件夹 名字一致
delete : /P 删除前prompt 会确认是否删除。 /s Delet from all subdirectories . /Q Quite mode 删除时候不会问
type Displays the contents of a text file or fiels 像linux 的cat
exit /b 与goto :eof 功能一样 退出程序
command
dir #show everything inside the folder
ver #show the version of Microsoft Windows
cls #clean cmd
pause #wait to press input
Data Type, varibles
Integer: 1 0 -1 -30 9000
Character: a b c d e
String: “Hey! My name is” (sometimes, we use 双引号,有时候不用双引号)
set varname=Howdy #把varname 等于 Howdy
%varname% #显示'Howdy' is not recognized as a internal or external command
set varname="Howdy" #加quotation mark
echo %varname% #显示'"Howdy"'
#even though it is string, it still interpret quotation mark which we don't want that
Environment Variables
windows/batch has some stored variables, we can access this variables. They are called environment variables because these are variables stored in the environment
注: 假如我在prompt 中运行batch script(test.bat), batch script中有set aab=Hello. 即使我run 完script, 只要不关闭prompt, aab会一直存在cmd 中, echo %aab% 会打印hello
set #显示all the variables whindows track of
echo %%COMPUTERNAME% #显示 电脑名字
set varname=Howdy
set #打出的environment variables 显示varname=Howdy
set var #打出所有environment variables starting with var
set USER #打出所有environment variables starting with USER
String Concatenation
set string=becks
set string+=wu #用+= string 依旧是becks
echo %string% #打印becks
#实际上,又建立了一个新的variable 叫string+
echo %string+% #打印wu
set string=%string% wu #string 现在是 becks wu (有空格)
%string% #显示'becks' is not recognized as an internal or external command
echo %string% #显示becks wu
Echo
echo Hello There #会打印出Hello There
echo "Hello There" #会打印出"Hello There"
echo #打印 echo is on
echo. #打印出一个konghang
Command Argument, Help
dir Desktop #显示Desktop的dir
vol ##显示C盘的volume Serial Number, default is C Disk
vol D: #显示D盘的volume Serial Number
help #show every command
help dir #give dir 的help 所有可以用的flag
dir /? #与help dir 效果一样
@Symbol
@ 作用: stop command from displaying within the prompt 在batch script中
@echo Hello Wolrd
echo Hello World
#上面两个作用一样
#比如文件中不想打印出ver
@ver, 只显示ver的结果,不会先打印ver, 再显示ver在cmd中,只显示ver的结果
@dir, 只显示dir的结果,不会打印dir 再显示结果在cmd中
Echo off
如果script用@echo off,不会display everything inside the batch, 只显示output
help echo #显示ECHO 可以 ON | OFF
echo /? #与上面作用一样
echo #显示ECHO is on.
echo off #stop display prompty
echo on #turn prompt back on
Escape Characters
%% scape %, ^<, ^> escape <>, ^^ escape ^
@echo off
set variable=PROBLEM
echo This is a %%variable%% #显示This is a %variable%
#显示 > < ^
echo ^<html^> #显示<html> 用^ escape <>
echo ^^ #显示^
Math
SET /A 表示数学
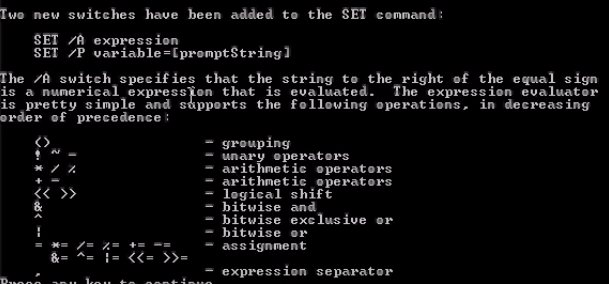
注: 在prompt 中可以用 % (mod), 但在script中,对于mod需要 % escape %
@echo off
set sum=1+1 #把1+1设置成了string
echo The sum is %sum% #This sum is 1+1
#可以用help
set /?
set /a sum=1+1
echo The sum is %sum% #This sum is 2
set /a sum=5 * 2
echo The multiplier is %sum% #This multiplier is 10
#下面的在prompt中可以用
set /a sum=10 / 2
echo The divider is %sum% #This divider is 5
set /a mod=10%3
echo The module is %sum% #This module is 1
#在script中
set /a mod=10 %% 3
echo The module is %sum% #This module is 1
Input
set /p 读取input from user
@echo off
set /p name=Please enter your name!
echo Your name is %name%;
#换行输入
echo Please enter your name! #第一行显示 Please enter your name!,第二行输入
set /p name=
echo Your name is %name%;
Label, Goto
batch won’t interpret when label is not starting position of each line
#echo off
:another
cls #belong to another
ver #belong to another
:label #everything below label is part of label
#label is belong to another
vol #belong to label
Goto
@echo off
echo This is the very beginning of the program!
goto :start #跳到start, print start, middle, end
goto :middle #跳到start, print middle, end
goto :end #跳到start, print end
:start
echo This is the START of the program!
#goto :end 跳到:end, 跳过middle
:middle
echo This is the MIDDLE of the program!
:end
echo This is the end of the program!
Comment
rem 会读取这一行的内容,slowdown your execution of program, :: comment, 但这也是label, 因为是label,必须是beginning of line
@echo off
ehco This is a script
rem This is a comment #rem 会读取这一行的内容 即使表示comment,slowdown your execution
help rem #显示REM [ comment]
:: This is comment/label! #comments, 但也是labels, 不会打印出来
Function
%~1 as the function first input
goto : eof, finish current job, if main exit, if function (label), return to main
endlocal: delete all variable being seen from setlocal
Group command & 在function 结尾 endlocal & set /a x=%x% + 1 , x会更改main 中的x
pass value to function default pass to function is string, 如果想pass value 加上是百分号 %y%
@echo off
goto :main #jump to main function
:function
echo This is another function
goto :eof
:main
echo Main function is being called!
call :function #call another function
echo End of main function
echo End of program
goto :eof #end of file, goto eof 会exit
Function Arguments
@echo off
goto :main #jump to main function
:say_something
echo I am saying %~1 and %~2
goto :eof
:main
echo Main function is being called!
call :say_something tiger boat #call another function, tiger is string, boat is string
goto :eof #end of file, goto eof 会exit
可以更改function的%~1 值,更改外面的variable
@echo off
goto :main #jump to main function
:function_return
echo Changing a variable
set variable=Value
goto :eof
:change_variable
echo Changing a variable
set %~1=Lunch
goto :eof
:main
echo Main function is being called!
echo %variable% #显示Echo is off, 因为没有variable
call :function_return
eco The variable is %variable% #显示The variable new value is Value
set new_var=Dinner
call :change_variable new_var
eco The variable is %new_var% #显示The variable new value is Lunch
goto :eof #end of file, goto eof 会exit
local variable: setlocal, endlocal
@echo off
:local_var
setlocal
echo Func says %p% #显示The says is 4
set x=30
echo Func says x is %x %#显示Func says X is 30
endlocal
goto :eof
:main
setlocal
echo Main function is being called!
set p=4
echo Main says p is %p% #显示Main says P is 4
call :local_var
echo Main says x is %x% #显示Main says X is (因为x在local_var中式local)
endlocal
goto :eof
script local scope: script不设置setlocal(不管是main 还是function, function 不设local,也会存进system_variable中), 只要不关闭prompt,script中 set的variable 设置的会在system_variable中
@echo off
goto :main
:main
set global_var=exisiting
goto :eof
#上面的file run了之后,global_var会存在system variable中
:main
setlocal
set global_var=exisiting
endlocal
goto :eof
return local, Group command & : 在function 结尾endlocal & set /a x=%x% + 1 , x会更改main 中的x
@echo off
goto :main
:add_one
setlocal
echo Performing ADD ONE on x
endlocal & set /a x=%x% + 1 #group command, 先执行endlocal, 再执行x = x+1
goto :eof
:main
setlocal
echo Main function is running
echo Setting X to 1 #显示Setting X to 1
set /a x=1
call :add_one
echo The value of X is now %x% #显示The value of X to 2
endlocal #x 不会存进system 当run 完code, 因为endlocal 删除了 x, 即使add_one set不是 local
goto :eof
@echo off
goto :main
:add_one
setlocal
echo Running 'add_one'
endlocal & set /a %~1=%~2 + 1 #group command, 先执行endlocal, 再执行x = x+1
goto :eof
:main
setlocal
set /a x = 1
set /a y = 50
echo Created variable X and set it to %x%
call: add_one y %y% #pass y as first variable, pass value of y as second variable
#如果pass y function 认为是string,
echo The value of y is %y% #显示the value of x is 51
endlocal #x 不会存进system 当run 完code, 因为endlocal 删除了 x, 即使add_one set不是 local
goto :eof
If
equ : ==
neq : !=
lss : < less than
leq : <= less than or equal
gtr : > greater than
geq : <= greater than or equal
if statement, 不用parathesis 来include condition 表示group command
else 需要在)的同一行接着,不能换在)下一个行 加else, 否则会报错
#echo off
goto :main
:main
setlocal
set /a food=10
set /a needed_food=10
if %food%==%needed_food% ( #beginning of if
echo We have enough food
) else (
echo We do not have enough food!
)
if %food% equ %needed_food% ( #beginning of if
echo We have enough food
) #end of if
if not %food%==%needed_food% ( #beginning of if
echo We do not have enough food
) #end of if
if %food% neq %needed_food% ( #beginning of if
echo We do not have enough food
) #end of if
if %food% leq %needed_food% ( #beginning of if
echo We have enough food
) #end of if
if %food% gtr %needed_food% ( #beginning of if
echo We more than enough food
) #end of if
endlocal
goto :eof
Nesting
@echo off
goto :main
:main
setlocal
set /a food=50
set /a needed_food=50
set /a people=10
set /a rations=5
set /a all_food=%people%*%rations%
if %food% geq %needed_food%(
echo We have a good amount of food!
if %all_food% leq %food% (
echo We have enough food for all %people% peoples!
)else (
echo We do not have enough food for all these people!
)
)else (
echo We do not have enough food!
)
endlocal
goto :eof
Delayed Variable Expression
在if statement 括号里,括号里是group command, in fact they are only one command. 如果用普通set 加上 %% 会报错 显示unexpected, 因为是one command, set 会在所有command 结束后才create variable,但是我们需要create variable right away to see if condition,需要加上setlocal enabledelayedexpension, 当call variable时候,需要用!, e.g. !food!, 对于echo 感叹号, 需要escape,e.g. Hello World ^^!
如果script a 有enabledelayedexpension, 即使script b 不说enabledelayedexpension, 但是script b被script a called, 所以b inherit a 的environment,也会有delayedexpension
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpension
goto :main
:main
setlocal
echo Hello World ^^! #需要^^ escape !, 打出 Hello World!
echo "Hello World!" #打出 "Hello World!"
set /a food=50
set /a needed_food=50
set /a people=10
set /a rations=5
if !food! geq !needed_food!(
echo We have a good amount of food!
set /a all_food=%people%*%rations%
echo !all_food!
if !all_food! leq !food! (
echo We have enough food for all !people! peoples!
)else (
echo We do not have enough food for all these people!
)
)else (
echo We do not have enough food!
)
endlocal
goto :eof
While
Batch 不支持while, 需要用label + goto
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
goto :main
:main
setlocal
set /a counter=0
set /a limit=10
:loop
if !counter! < lss !limit! (
echo !counter!
sete /a counter=!counter!+1
goto :loop
)
echo.
endlocal
goto :eof
For Loop
/l: %%g in (start, step, end)
/d : directory
%% : for %%i in 用于batch script (.bat)中 % : for %i in 用于prompt console 中, 不在script中
basic
in batch script, specify %%variable instead of %variable. set () 中用space 分开表示不同的需要loop 的是variable, 如果用引号就表是set中只有一个variable需要loop 的
For Loop Number Syntax: for /l %%g in (start, step, end) . end 是include的
break For loop : 用 label + goto
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
goto :main
:main
setlocal
set string=Heloo world^^!
echo !string!
set /a test=3
for %%g in (1 2 3 4 5) do ( #需要%% 来表示variable,
echo %%g
if !test! equ %%a (
echo !test! in %%g
)
)
for %%g in (a b c d e) do ( #需要%% 来表示variable,
echo %%g
if !test! equ %%a (
echo !test! in %%g
)
)
for %%g in (This is a block of words) do ( #需要%% 来表示variable, space分开不同的string
echo %%g #打印第一行This, 第二行is, 第三行 a ....
if !test! equ %%a (
echo !test! in %%g
)
)
for %%g in ("This is a block of words") do (
echo %%g #打印第一行"This is a block of words" 有引号的
if !test! equ %%a (
echo !test! in %%g
)
)
for /l %%g in (1, 1, 20) do ( # /l l-type, start, step, end, (1, 1, 20), 从1到20 每一次增加1
echo %%g
)
for /l %%g in (0, 5, 20) do ( # 0 -> 5 -> 10 -> 15 -> 20
echo %%g
)
#Break
for /l %%g in (1, 1, 10) do (
if %%g equ 5 (
goto :loop_end
)
echo %%g
)
:loop_end
echo This is a End of Loop^^!
endlocal
goto :eof
directory, file
/r display all folders and files and it will recursively loop all subfolder
Directory:
/d: directory, 不能显示file,只能显示directory
* : wildcard with /d, display every directory
不能用. (表示现在的directory),需要用wildcard *
File:
不用/d Flag
* : wildercard , display every file
File Content
/f : get info from file
default delimiter For loop is space
“delims=/”: 设置delimiter as / ; “delims=,”, 设置delimiter as ,
“skip=3”:读取时候跳过三行, 第1行读完,读第5行,再读第9行
“tokens=2,3,4 delims=,”: 设置delimiter as 逗号, 并读取每一行的第2,3,4 field
如果用%%g 在for loop, %%g, %%h, %%i, %%j, %%k 分别表示first,second,third,fourth,fifth field
/f + ’command‘ : 用单引号在括号中,可以用for loop 来loop command
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
goto :main
:main
setlocal
#Directory
set string=Heloo world^^!
echo !string!
set /a test=3
for /d %%g in (*) do ( #/d display directory 但不display 任何file, * wildcard
echo %%g
)
for /d %%g in (D*) do ( #/d display directory, D* any folder start with D
echo %%g
)
for /d %%g in (D*s) do ( #/d display directory, D*o any folder start with D and end with s
echo %%g
)
for /d %%g in ( . ) do ( #. 表示现在directory, 不会显示任何东西,因为需要用* wildcard
echo %%g
)
#File
for %%g in ( * ) do ( #display file 但不display 任何directory, * wildcard
echo %%g
)
for %%g in ( *.bat ) do ( #display all batch file
echo %%g
)
#File Content
#delims, skip, token,
for /f %%g in ( banks.csv ) do ( #display content from csv, 但是因为default delimiter 是space,所以csv 每行只打印第一列然后就停了, 因为逗号后面和后面content 有空格
echo %%g
)
for /f "delims=/" %%g in ( banks.csv ) do ( #设置delimiter as /, display all content from csv
#delims=/ display entirety of that of page, 会一行一行打印出来,遇到eof跳行
echo %%g
)
for /f "delims=/ skip=3" %%g in ( banks.csv ) do (
#/ skip 中间有空格,skip=3 表示skip 3行,结果会打印第1行,第5行 (2,3,4 skip 掉), 第9行...
echo %%g
)
#tokens allow you to get pieces of information,
for /f "tokens=*" %%g in ( banks.csv ) do (
#* get all information from the file
echo %%g
)
for /f "tokens=2,3,4 delims=," %%g in ( banks.csv ) do (
# tokens=2,3,4 只需要第二列,第三列,第四列所有的数据
echo %%g #但只打印第二列的数据,因为 %%g 表示第二列,%%h 表示第三列,%%i 表示第四列
)
for /f "tokens=1-9 delims=," %%g in ( banks.csv ) do (
#tokens=1-9第一列只到 第9列的, %%g 表示第一列, %%h 第二列, %%i 第三列, %%j 第四列, %%k 第五列
echo %%g, who is %%i and bank at %%j
)
#比如我们comment line 不想让它进for loop, ignore them
for /f "delims=/ eol=#" %%g in ( banks.csv ) do ( #当line start with #, skip the line
echo %%g
)
#loop command
for /f "delims=/" %%g in ( 'cd' ) do (#loop through command cd,
echo %%g #显示现在路径
)
for /f "delims=\ tokens=1" %%g in ( 'cd' ) do (#比如cd 是 C:\Users\ 因为\分行, 第一行就是C:, 然后只要第一个field
echo %%g #只显示C
)
#string + token : to get piece of string
for /f "tokens=1-9" %%g in ("This is a nice sentence") do (
#tokens=1-9 to extract first to ninth term of the string
echo %%g %%h %%i #显示This is a
)
set string=This is a nice sentence
for /f "tokens=1-9" %%g in ("!string!") do ( #与上面的for loop 功能 一样
#tokens=1-9 to extract first to ninth term of the string
echo %%g %%h %%i #显示This is a
)
endlocal
goto :eof
Redirection
: standard output
: appened
2> : standard error output
choice: ask you yes or no, 如果输入Y/N 是standard input
| : pipe, redirect the output of one command to the standard input of another command
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
goto :main
:main
setlocal
::stdout 1 #it is a comment
::stderr 2 #it is a comment
dir /b > new_file.txt #dir /b : show a simple output of all stuff in current directory 并输出到new_file.txt
dir /b 2> new_file.txt #dir /b 2: only send standard error to the file
dir /b > new_file.txt 2>&1 #先output dir /b 到new_file.txt, 再output std err 到new_file.txt
# >&1, 表示send output 到the file we already sent, 注意不要有空格
echo Ahything we want^^! > new_file.txt #把Anything we want! output 到new_file.txt
echo That was hilarious^^! > new_file.txt #append That was hilarious 到new_file.txt
#choice
set file_name=new_file.txt
echo y> !file_name!
#echo y> 把y output 输出
#echo y > 把y+空格 output 输出
choice < !file_name! #把y send 到choice
# pipe
echo y|choice #pipe y 到 choice
endlocal
goto :eof
Working with File
dir *.bat #只显示所有的.bat的file
D: #比如现在 在C盘,nagivate 到D盘,不用cd, 直接打D:
#move
move new_file.txt other_name.txt #move 相当于rename file 从new_file 变成other_name
move new_file.txt ..\ #把new_file 移动到 parent class folder
move ..\new_file.txt . #把parent folder中的new_file 移动到现在这个folder
move /Y folder folder_2 #把folder 给rename 成 folder2
#copy
copy new_file.txt other_file.txt #把new_file内容 copy 到other_file.txt, 如果没有other_file.txt 生层一个新的file
copy *.txt folder #copy 现在所有的txt file 到新的folder,名字与现在被copy 的保持一致
#Append
copy new_file.txt+other_file.txt new_folder #把现在directory中new_file 和other_file内容, 一起copy 到新的在new_folder 这个folder 中的new_file.txt
#如果不想用append, 用for loop
for %i in (new_file.txt other_file.txt) do (
copy %i new_folder
)
copy new_file.txt D: #把现在文件夹下的new_file.txt copy到D盘
#delete
del file.txt #删除file.txt
del /P file.txt #删除file.txt 与上一行不同的是,这个删除前会让你确认
del /S *.txt #删除现在folder 和子folder 中所有的.txt file
#type
type new_file.txt #打印所有content 到screen
Customized Prompt Console
color 第一个参数表示background color, 第二个参数表示foreground color 如果foreground 和 background 颜色一样显示 errorlevel to 1,但是color 只能暂时更改,当更改后,color会恢复原来的default. 如果想永远更改,需要右键properties, 但是右键properties改完后,比如你run admin的command 颜色还是default. solution: 可以create cmd shortcut 在desktop上,这样以后每次点这个short cut,更改它的properties 会固定了
command的properties 可以改比如按 ↑ 可以回多少个之前的command,buffer 存之前多少个command
color /? # 查color command syntax
color background-color foreground-color #syntax
color fc #背景是bright white, 字体是light red
color F0 #背景是bright white, 字体是Black
color #恢复default 背景字体颜色
colormsg c "Hellworld" #print Helloworld in red
colormsg 3a "Helloworld" #print Helloworld 字体是Aqua, 背景是Light Green

prompt
@echo off
#因为prompt command 会change prompt 不能加setlocal 和 endlocal
prompt $C$S%USERNAME%@%COMPUTERNAME%$S$F_$P$S$G$S #$C left parenthesis, $S space, $F right parenthesis $P current drive and path, #G > greater-than sign, $_ 换行
#上面会改变prompt 每次输入时候,先打印 ( becks@windows ) 第二行会打印出现在的path >
prompt #把prompt 改成default
Substring
!var:~a,b!
a>0 : 表示从左向右的第a个位置开始
a<=0 : 表示从右向左的第a个位置开始
b>0 : 表示从位置a开始 向右侧b个substring
b<0 : 表示从位置a开始 向左侧b个substring
!var:cat=dog! #把var中所有的cat 用 dog 代替
%~I - expands %I removing any surrounding quotes (“)
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
goto :main
:main
setlocal
set var=This is totally a string
echo !var:~8! #print: totally a string
echo !var:~2! #print: This is totally a string
echo !var:~8,7! #start at position 8 and length 7, print totally
echo !var:~0:4! #This
echo !var:~0:-6! #start from end and length 6, print string, -6 length 从右向左, print string
echo !var:~6:6! #start from 倒数第6位,然后从左向右的六个substring
#substitution
set var=The cat in the hat ate the mat
set var=!var:cat=dog #用dog 代替所有的 cat, 并assign 给var
echo !var:hat=raincoat! #用raincoat 代替所有的hat
echo !var:hat=! #把所有的hat 去掉
#string quotation
#useback + %%~g: only get the string surround 比如 "More information, more " word " 不会移除more 和word之间的引号,只移除两边的引号,
set string="TEXT"
for /f "useback tokens=*" %%g in (!string!) do set string=%%~g #string 是被remove双引号,
endlocal
goto :eof
create string function
#命名file 为create_string.bat
@echo off
#Create String Function
set string=%2
set /a takeaway=5
for /f "useback tokens=*" %%g in ('%string%') do set string=%%~g
echo %2 > %TEMP%\tempfile.txt #%TEMP% is the temporarily folder in windows
for %%g in (%TEMP%\tempfile.txt) do (
if %string% equ %%~g ( #
set /a takeway=3
set /a @1_length=$$~zg - 5 #$$~zg to get length of vriable, -5 to get rid of some character which we don't care about
)
del %TEMP%\tempfile.txt #delete the temporary file
set %1=%string% #设置第一个传入function 的参数
command script
#有了上面的create_string.bat
> create_string.bat four "lines"
> echo %four% #返回lines (没有引号)
> echo %four_length% #返回5
#有了上面的create_string.bat
@echo off
setlocal EnableDelayedExpansion
goto :main
:main
setlocal
call create_string var "This is some text!"
echo !var!
echo !var_length!
endlocal
goto :eof
Array
@echo off
#even if we don't say setlocal enabledelayedexpansion, but we will use !var!, because it inherit the environment from the script calling
:: create_string name "delimiter" "content"
:: create_string grocery_list " " "Apples Bananas Meat" #
goto :main
:main
call create_string delimiter %2
call create_string content %3
set /a offset=0
set /a index=0
goto :eof
W
chmod 755 file.txt #give user read, write execute(7), give both group and othe group read and execute access
Bash Script
Script: txt file contain sequence of command
nano myscript.sh #open editor
#! /bin/bash #需要contain location of bash
which bash #会告诉哪里有bash,give location
./myscript.sh #./ 是去run bash script
#显示permission denied 因为file created not have execute permission
#先给permission
chmod +x myscript.sh #give permission for all groups
./myscript.sh #显示会成功
which & what
which: where software/command located
what: display short manual page description
#which ls #give location where ls command located
which firefox # location of bash
which bash # location of bash
whatis ls # short description, to know what ls doing command
whatis grep #short description, to know what is grep command
useradd
create user
useradd the_name_of_user #syntax
sudo useradd mark -m -s /bin/bash -g users -c "my comment"
#-m: create default home directory for this user
#-s /bin/bash allow usesr to use shell
#-g assign group, default group is users
#-c "my comment" provide comment to user
#-G assign/give user defined group
#sudo: because you don't want anybody create user, only root can create user
sudo passwd mark #change password for user
userdel
sudo userdel mark #delete user mark (username, password, data), not delete home directory for user
sudo userdel -r mark #delete user (home directory, username, password, data)
sudo -r /home/mark/ #remove all the data from user
groups, groupadd, groupdel
group show which group is currently user connected to
groups #show which group is currently user connected to
cat /etc/group #show all the group in your system, group <-> user connected to
sudo groupadd Java #add newgroup in system
sudo groupdel Java #delete existing group
#-a add user to group, -d remove user from group
sudo gpasswd -a mark Java # add mark to the Java group
sudo gpasswd -d mark Java #remove user from Group
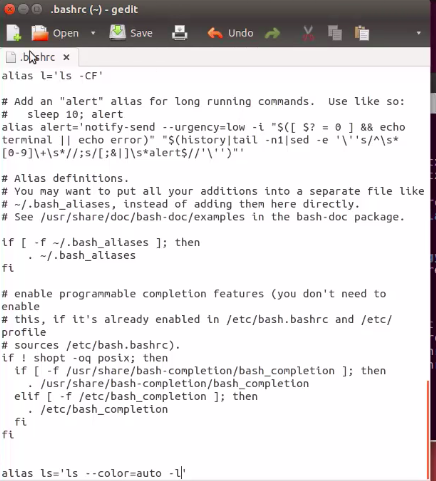
bashrc
bashrc is a script executed whenever a new terminal session start in interactive mode
some linux system, .bashrc file exist when a new terminal session start. Some not
Bashrc file is used for setting up environment variable such as Java. When use git, which repo you checked or cloned, use Bashrc
ls -a #在home directory ls -a 可以看见有.bashrc
nano .bashrc #查看.bashrc
gedit .bashrc #查看 .bashrc
可以修改 .bashrc file 比如加上alias ls=’ls –color=auto -l’, 之后open new terminal, 输入ls, 显示long list of ls
du, df, free
View Resources
df #the amount of disk space being used by your file system
df -h #the human readable output, 显示多少G, M, k
du #estimate and display the disk space used by files in details
du -h #human readable format
du -sh #-s summary 只给你现在所在directory 文件所占的大小
sudo du -sh #用sudo 原因是因为可能有的file permission denied 需要用sudo
du -sh /etc/ #show summary used space by etc folder
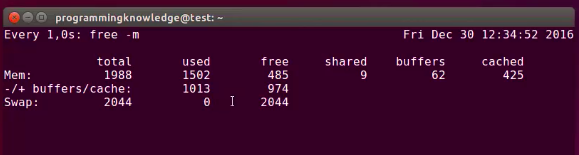
free #display the total amount free and used physical and swap memory in the system as well as buffer in the kernel
free -b #-b btye, -k KB, -m MB, -G GB, -T TB
watch
run scripts for command at a regular interval or repeatedly
watch free -m #可以看见几秒会更新一次
Ctrl + C #exit watch command
watch -n 1 free -m #让free -m command run every 1 second
watch -n 0,5 free -m #让free -m command run every 0.5 second
head tail
Head: output the first part of the file Tail: output the last part of the file
head log.txt #show first 10 line of file
tail log.txt #show last 10 line of file
head -n3 log.txt #show first 3 lines of file
head -3 log.txt #跟上面一样
tail -n3 log.txt #show last 3 lines of file
tail -3 log.txt #跟上面一样
tail -f log.txt #output last 10 lines of file. watch the file, whenever file change, will show last 10 lines of code
ctrl + C #exit
head log.txt kern.log #先print 10 lines of log.txt 再print 10 lines of kern.log
head -3 log.txt kern.log #先print 3 lines of log.txt 再print 3 lines of kern.log
find
find location -name file_name #syntax
find /home/ -name test.sh #-name search by name, return directory
find /home/dir1 -name test.* #search in /home/dir1 folder by name, any file start with test. 可以是.txt, .sh
find /home/dir1 -name *.txt #search any file extension is txt
find / -name dmesg #search in the root directory, 也许有permission error 因为有些directory 不允许access
sudo find / -name dmesg
find /home -mtime -1 #look at the file created 1 days before, 也可以用加号,+1, + 2
wc
wc: world count, print a count of lines, words and characters for each files
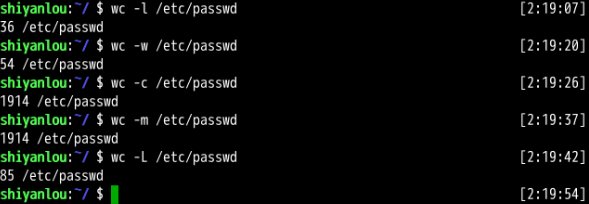
wc test.txt #打出#lines, #words, #characters
wc -c test.txt #只打出#characters
wc -l test.txt #只打出#lines
wc -w test.txt #只打出#words
wc -L test.txt #只给出number of character in longest line
1, 6, 42: 1 number of line, 6 number of words, 42 number of characters
cal
show conventially formatted calendar on your command line
cal #显示calendar, weekday on the top
ncal #显示calendar, weekday on the left
cal 2016 #显示2016的calendar
cal 2 2016 #显示2016年 2月 calendar
cal -3 #give you current month, previous month and next month calendar
#default 是 -1, 比如cal, 等于cal -1
date
used to print out and change system date and time information
date #print 现在系统的时间
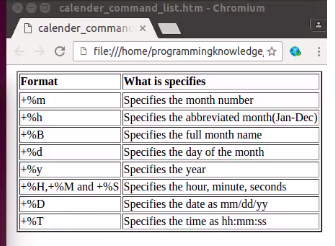
date -s "11/20/2003 12:48:00" #设置system time 为 11/20/2003 12:48:00
date +%d%h%y #显示13Jan17
date +%d/%h/%y #显示13-Jan-17
man date #可以显示详细的date format的格式
date "+Date: %m/%d/y%n" #显示01/13/17 %n 是空行线
设置时间格式
Run Multiple Terminal(; && || )
#; sequence matter
ls; pwd #先run ls 再显示pwd
date; cal ; pwd #先run date, 再run cal, 再pwd
#如果有中间一个command 是错的
date; CAL; pwd #date, pwd run 成功了, CAL 会显示command not found
#&& sequence matter, 顺序一个接一个
ls && pwd && date && cal #先run ls, 再pwd, 再date, 再cal
ls && CAL && pwd #先run ls, CAL error, not run pwd
ls || pwd #如果第一个command 成功了,不会run 第二个command
CAL || pwd #CAL command failure, pwd 会被run
Difference: ; run every command regardless success/failure of each command. && 如果中间的failure, does not go to the next command
apt-get
apt-get(urbantu): install, uninstall, update packages. apt: advance packaging tool
对于centos: 用yum, dnf instead of apt-get
sudo apt-get update #resync your local package file to the server package file, update all the packages
java -version #check if java installed, and if so check version
php5 -version #check if php installed, 如果没有install 会给出install的hint
sudo apt-get install php5 #安装首先what is required extra dependency to install php5, 也会显示多少space required to install
php5 -v #显示php5 version
sudo apt-get remove php5 #remove php5
sudo apt-get remove --purge php5 #remove all configuration file related to php5
sudo apt-get autoremove #auto remove the dependency which required for the package(php5) and no longer needed for other packages
ifconfig
ifconfig: interface configuration: used to view and change network interface configuration on your system
ifconfig #show you some output
ifconfig eth0 #only show eth0 interface
#up, down to disable internet connection
sudo ifconfig eth0 down #internet connection will be down
sudo ifconfig eth0 up #enable internet
ethO: wired internet cable
WLAN0: wireless internet connection
0: is the first internet interface. 如果有multiple internet interface, 显示eth1, or WLAN2
l0: loop back interface. An interface that system use to communcate to excel
tar
tar: Tape Archive, compress and extract file
tar -cvf test.tar test #cvf: create verb, f filename, 把test folder compress 成命名为test tar 压缩文件
tar -xvf test.tar #xvf x: extract v verb, f filename, 把test.tar extract 压缩文件
#有时候用 tar.gz gz stands for gzip format
tar -cvfz test.tar.gz f.txt #z 表示生成gz file, z必须在c flag 之后, 压缩文件成tar.gz
tar -xvfz test.tar.gz f.txt #解压 gz 文件
man tar > tar.txt #把tar 的man output 到tar.txt 中
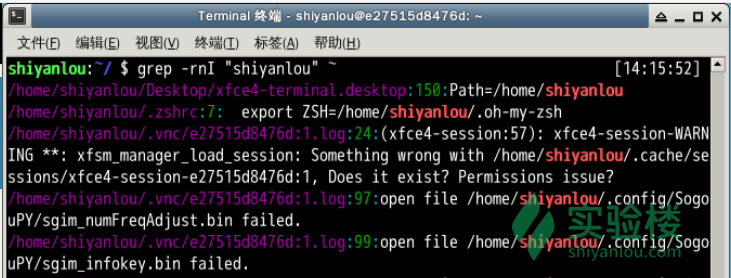
grep
grep: global regular expression print. can be used to search pattern / word in a text file or a number of text file with grep command
#
man tar > file.txt
grep "options" file.txt #keyword I want to search and file name,
#grep 是case sensitive的, 上面的search options 不会search Options,
grep -i "options" file.txt #make search not case sensitive, 也会search Options
grep -n "options" file.txt #在file 中search并显示file.txt的options, 并显示在哪行
grep -n "Some options" file.txt #在file 中search并显示Some options
#used in multiple files
grep -n "Some options" f1.txt, f2.txt f3.txt f4.txt #在多个file 中search并显示Some options
grep -n "Some options" * #在现在folder中的所有file search并显示Some options 的行
grep -nv "Some options" f1.txt #显示f1.txt 不包含Some options的行
grep -help #显示有的flag, options 用grep command
netstat
netstat is to display network connection, routing tables and a number of network interfaces, and view network protocal states
netstat -a #show all connections which are available on your system whether it is TCP or UDP or UNIX connection,
#上面aslo display the status if it connected, listening, or established
# | means after | whatever second command is used will implement the output of the first command
netstat -a | less #use the output of netstat to display with less command
netstat -at | less #-t means just show the TCP connection
netstat -au | less #-u means just show the UDP connection
netstat -l | less #-l means just show listenning state
netstat -lt | less #-lt means just show listening and TCP connection
netstat -lu | less #-lu means just show listenning and UDP connection
netstat -s | less #-s show the statistic of connection, you can see which type of connection it is and properties of the packet what is happening
netstat -st | less #-st show the statistic of TCP connection
netstat -su | less #-su show the statistic of UDP connection
netstat -pt | less #-pt show PID of TCP connection
netstat -px | less #-px show PID of UNIX connection
netstat -n | less #-n show the numeric port of connection
netstat -c # show the connection continuously, it refresh by itself
netstat -ie #-ie extended interface, it is the same output as ifconfig
netstat -an | grep ":80" #-an show numeric port of all conection and search which port has :80